Portfolio analysis is the study of various business areas to identify promising and redistribution company resources. The conclusions of the analysis can be as follows: assessment of the need to distribute investments within the company, evaluation of the effectiveness of the redistribution of labor and changes in the organizational structure of the enterprise, the choice of the vector of development.
Portfolio analysis procedure:
- Divide the company's activities into strategic units
- Determine the competitiveness of business units in the market (potential, position of the company in the market, competitive analysis)
- Analysis of the company's activities (resources, personnel competencies, risks)
- Setting goals
- Working with portfolio matrices
- Development of strategies based on portfolio matrices
The portfolio matrix is the system by which the analysis is carried out. Like any Martrix, a portfolio matrix is a collection of rows and columns at the intersections of which there are strategic elements. Rows and columns must meet various business criteria: market share, investment, cost, and more. The choice of a portfolio matrix depends on the goals of the enterprise and the market situation.
One of the most popular matrices is the BCG matrix. It is a chart that was created by Bruce D. Henderson for the Boston Consulting Group in 1970 to help corporations to analyze their business units, that is, their product lines. The size of the vertical in this matrix is set by the display of the size of the question, and the size of the vertical is relative to the distance of the market. This relation should define comparative competitive positions in the future.
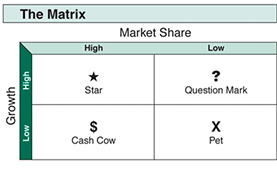
BCG Matrix (Henderson, Bruce D. "The Product Portfolio". Retrieved 16 May 2013.)
"Stars" are taking a leading position in the fast growing industry. They bring significant profits. However, "Stars" require large resources to finance the continued growth, as well as serious control over the leadership. The strategy of "Star" is aimed at increasing or maintaining a market sharing. As the speed of development decreases, the "star" is transformed into a "Cash Cow".
The "Сash Cow" is the main one in a stable market. Since sales are relatively stable at no additional cost, then this product costs more than is needed to maintain it. The strategy of the "Cash Cow" is aimed at long-term maintenance of market position.
The "Question Mark" is characterized as a weak drive on the market in the developing industry because of its small share. Competitors occupy the leading position on the market. To maintain or increase the share on the market in conditions of strong competition, more funds are required.
"Pet" have a limited volume of sales on the market. These products did not succeed in winning the sympathies of consumers, and they lose to competitors in various dimensions (market share, the size and structure of the consumer, product processing, etc.). The strategy of "Pet" is included in the weakening of efforts in the market or liquidation.
***
Other popular matrices include the Arthur D. Little Consulting Matrix; Shell Policy Matrix; Ansoff matrix; Abel matrix.